Choosing the right ceramic coating can be more complicated than you think, especially with so many coating products on the market. If you are a novice, you may feel confused when facing ceramic coatings, enamel coatings, Teflon, and other types of coatings? Not sure which one is right for your needs. People who know a little about ceramic coatings may be entangled in ceramic coatings vs. graphene coatings and wax coatings. Don’t worry! Let me help you clarify these misleading differences between similar coatings today to help you make the right judgment for your painting project.
Which is Better, Graphene Coating or Ceramic Coating?
If you are exploring cosmetic protection for your car or other surfaces, you may have come across two options: graphene coatings and ceramic coatings. Both options sound like they’ll protect your car’s paint, but which one is better? I won’t go into detail about ceramic coating, I have already explained it before, and interested friends can go to our other blog to learn more about it in detail.
Click to view detailed explanation of ceramic coatings.
Graphene coatings are a relatively recent innovation in automotive paint protection. It’s derived from graphene, a single layer of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice. Known for being extremely thin, light and strong, graphene has quickly attracted attention for its remarkable properties. Andre Geim and Kostya Novoselov isolated graphene back in 2004 and won the Nobel Prize in 2010 for this research. Today, graphene coatings have become popular in the car detailing community, with brands such as Adam’s Polishes and Ethos Car Care welcoming them.
Graphene coating concept
When used as a coating, it forms a durable coating with the following characteristics:
- High water contact angle, water beads form effortlessly from the surface, reducing water spots and streaks.
- Graphene coatings can withstand higher temperatures than ceramic coatings.
- Anti-static, dust and dirt are less likely to stick to the surface, keeping it cleaner longer.
- Graphene coatings can bend slightly with the surface and are less likely to crack and break.
Look familiar, right? Doesn’t it feel similar to ceramic coatings? But there are actually differences between them.
Comparison of Graphene coatings and Ceramic Coatings.
The main differences between graphene coatings and ceramic coatings are their performance, longevity and user experience. Ceramic coatings have long been the industry standard for surface protection, enhancing gloss and providing excellent protection against UV rays and minor scratches.
Although ceramic coatings are hydrophobic, they can sometimes retain some water stains due to their electrostatic properties, and their effectiveness may decrease over time if exposed to harsh conditions. In contrast, graphene coatings are more hydrophobic due to their antistatic properties, allowing water to bead up from the surface more efficiently while minimizing water spots. In addition, graphene coatings are also more heat-resistant than conventional ceramic coatings, which allows them to help car paint cope with hot climates or high-temperature environments.
And applying ceramic coatings requires more preparation before painting to avoid unnecessary streaks or high spots forming after the coating cures. Using graphene coating is much simpler, even beginners can use it easily.
In terms of service life, ceramic coatings can provide reliable protection for 2-5 years under the premise of proper maintenance. But graphene coating lasts longer because it has better resistance to oxidation and environmental wear.
| Graphene Coating vs Ceramic Coating | ||
|---|---|---|
| Feature | Graphene Coating | Ceramic Coating |
| Durability | Long-lasting, better oxidation resistance | Proven longevity (2–5 years) |
| Hydrophobicity | Excellent, anti-static properties | Excellent, but prone to water spots |
| Heat Resistance | Superior, withstands higher temperatures | Moderate |
| Gloss | High, but slightly less reflective | High, mirror-like finish |
| Ease of Application | Easier, forgiving for beginners | More precise, requires careful preparation |
| Cost | Typically more expensive | More affordable and widely available |
To sum up, graphene coating can often be regarded as a high-end product of ceramic coating. If you like mirror-like gloss and proven general surface protection performance, it is recommended to choose ceramic coatings. Otherwise, it is recommended that you consider graphene coatings as conditions permit.
Which is Better, Ceramic Coating or Wax?
As someone who values keeping surfaces, especially cars, looking their best, I’ve seen many friends debate whether to use wax or ceramic coatings.
Over the past few decades, wax has been a popular choice among car enthusiasts and everyday users. In particular, wax coatings containing natural ingredients such as carnauba wax or synthetic polymers can form a thin sacrificial barrier on the surface of a smooth substrate, giving it gloss and short-term protection.
Both wax and ceramic coatings offer protection and enhance appearance, but there are differences in their ingredients, longevity, and performance.
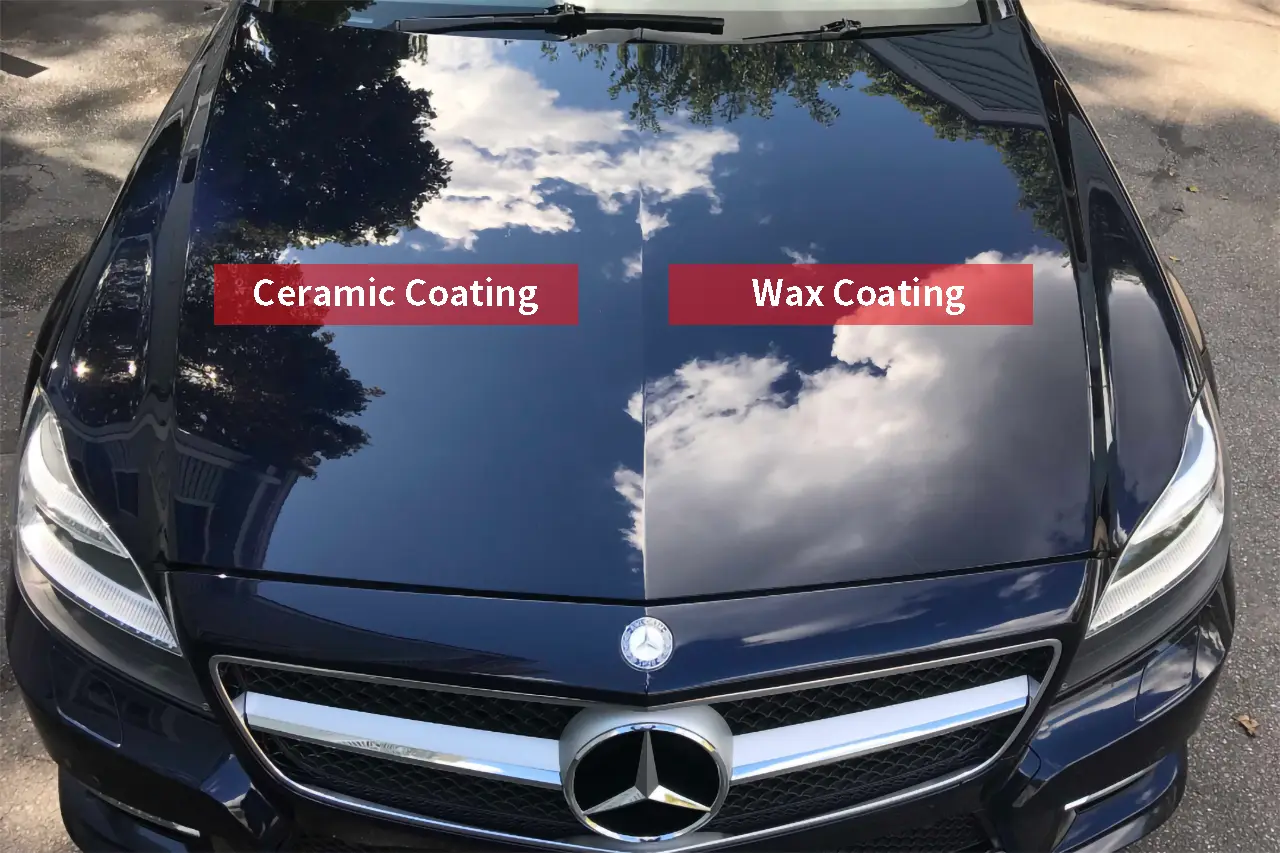

Ceramic Coating or Wax
- How long the effect lasts:
The wax only lasts a few weeks before it needs to be reapplied. Factors such as weather, cleaning frequency and surface exposure can shorten its lifespan.
Ceramic coatings chemically bond to surfaces and can provide protection for a year or more. The prerequisite is that sufficient time is given for the ceramic coating to cure. - Protection level:
Wax provides a physical layer of protection against microscopic contaminants such as dust and water stains. However, the protection effect against ultraviolet rays, chemicals and severe weather is poor.
Once cured, ceramic coatings offer excellent resistance to UV rays, chemicals, heat, and oxidation. Its hydrophobic nature causes water to bead and roll off, reducing dirt buildup. - Appearance:
Waxes are known for their rich, deep sheen and warm finish.
Ceramic coatings offer a finish that leans toward a smooth glass surface, extremely clear and shiny, emphasizing a clean and modern aesthetic. - Easy to use:
Wax is easier to apply and remove, making it ideal for DIYers or quick touch-ups. Applying ceramic coatings, however, requires more preparation and skill to deliver the best results. - Cost:
Whether it’s the purchase of the wax product or the cost of application, the cost of investing in a single application of wax is lower.
The initial investment in applying ceramic coatings is relatively high, but if you extend the timeline, you will find that its cost-effectiveness is also good.
Which of them is better? The answer depends on what you value most. Take the example of car paint protection: the main function of car wax is to beautify the car paint in the short term and add a warm sheen to the car. In addition to enhancing the surface gloss, ceramic coatings can also form a protective layer to improve durability, but the investment cost is higher and the construction is more complex.
If you have the time and like to do regular maintenance yourself, then affordable, easy-to-apply wax is the best choice. For those who want advanced durability and are willing to invest in a professional application, ceramic coating will be more in line.
| Feature | Wax | Ceramic Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Natural carnauba wax, synthetic polymers, or a blend of both | Silicon dioxide (SiO₂), titanium dioxide (TiO₂), and polymer-based nano coatings |
| Longevity | 1–3 months | 2–5 years (depending on application quality) |
| Protection | Basic protection against dirt, water, and minor UV exposure | Advanced protection against UV rays, oxidation, chemicals, and heat |
| Hydrophobic Properties | Moderate water repellency | Superior water beading and self-cleaning effect |
| Appearance | Warm, deep gloss with a rich finish | High-gloss, sleek, and reflective “glass-like” look |
| Ease of Application | Easy to apply and remove, suitable for DIY use | More complex application, best applied professionally |
| Durability | Wears off quickly and requires frequent reapplication | Strong chemical bond to surface, resistant to wear and tear |
| Cost | Low initial cost, but frequent reapplication adds up | Higher upfront cost, but long-term cost efficiency |
| Reapplication Frequency | Every few months | Every few years |
| Can Be Layered? | Yes, can be layered over itself or ceramic coating | No need for layering, but wax can be applied on top |
Can wax and ceramic coating be used together?
Of course! While ceramic coating provides a long-lasting protective base, applying wax on top can enhance the warmth and depth of the surface shine. Keep in mind that wax is temporary and will not adhere to the surface as long-term as ceramic coating. This is why when the two are combined, the ceramic coating is applied on the bottom of the wax as the base layer.
The Difference Between Ceramic Coatings and Enamel Coatings, Teflon.
Ceramic coatings, enamel coatings and Teflon all aim to provide durable, heat-resistant protection for surfaces, which can lead to confusion for some people who are new to protective coatings. But their core ingredients result in each having a unique highlight.
- Ceramic coatings are protective coatings based on nanotechnology compounds such as silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or titanium dioxide (TiO₂). Once applied to a substrate, they chemically bond to the substrate to form a durable, clear barrier that resists minor scratches, UV rays and high temperatures. Its outstanding hydrophobic properties make it particularly popular in car detailing, which can enhance gloss and protect the surface from dust and dirt. Compared with enamel and Teflon, ceramic coatings are superior in durability and resistance to extreme temperatures.
- Enamel coatings are created by fusing powdered glass made of inorganic materials and metal oxides to a substrate at high temperatures. After curing, it forms a smooth coating that is highly resistant to wear and corrosion. Enamel coating has higher hardness and wear resistance than ceramic and Teflon, but its internal components lack the chemical bonding properties of ceramic coatings. Because of its high hardness, it can easily break if hit hard. Enamel coatings can be formulated to achieve a glossy, slightly textured effect as needed.

- Teflon, also known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), is a synthetic fluoropolymer known for its non-stick properties. Like enamel coatings, Teflon does not chemically bond to the surface, but instead forms a physical layer with a matte finish. Teflon is highly resistant to chemicals, friction and moderate temperatures, making it ideal for cookware, machinery and aerospace components. However, Teflon has limited durability in high-friction environments compared to ceramic and enamel coatings.
It can be seen from the basic ingredients of these three coatings that they have different uses and different functional highlights.
| Comparison of ceramic coatings, enamel coatings and Teflon | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Feature | Ceramic Coatings | Enamel Coatings | Teflon (PTFE) |
| Composition | Silicon dioxide (SiO₂) or titanium dioxide | Fused glass particles | Polytetrafluoroethylene (Fluoropolymer) |
| Durability | Highly durable, long-lasting | Very hard, moderate durability | Resistant to chemicals, moderate wear |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 1200°F (650°C) | Moderate (up to 400°F or 200°C) | Up to 500°F (260°C) |
| Hydrophobic Properties | Excellent | Minimal | Moderate |
| Non-stick Ability | Moderate | Low | Excellent |
| Finish | High-gloss, sleek | Glossy, textured | Matte, functional |
| Applications | Cars, industrial tools, electronics | Cookware, bathtubs, architectural surfaces | Cookware, machinery, aerospace parts |
| Primary Weakness | Expensive, requires professional application | Prone to chipping under impact | Wears down faster with high friction |
Ceramic coatings, enamel coatings, and Teflon each have their own advantages and disadvantages depending on the specific application needs. If you need to face extreme heat and ultraviolet rays, ceramic coatings are undoubtedly the best choice. If you need to face frequent friction (non-impact), enamel coating is preferred. And for nonstick properties or low-friction surfaces, Teflon is still unbeatable. Knowing your primary needs will enable you to make the right choice.
At this point, I believe you have a clear understanding of the differences between ceramic coatings and other common coatings, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and how to choose the coating that suits you best. Before purchasing the right coating product, be sure to consider all factors comprehensively to ensure that you find the most suitable solution for you. Of course, I’m sure some vehicle enthusiasts will change their minds after a while, such as trying to replace the old ceramic coating with a graphene coating. In any case, the source base coating needs to be removed (click to see how to remove the ceramic coating) to ensure that the new coating can better play its role.
If you are still looking for a suitable ceramic coating supplier or local coating service provider, you may wish to use the filtering function of our website to easily find and compare different coating products and services. Welcome to share your experience or leave any questions in the comment area, we will be happy to provide you with further assistance.
FAQs
How long does ceramic coating last?
Typically, ceramic coatings last between two and five years, depending on the quality of the coating product, how well it is used, and how it is maintained. High-quality coatings will last longer if properly maintained.
What materials are used in ceramic coating?
Ceramic coatings are primarily made of silicon dioxide (SiO2) or titanium dioxide (TiO2), and sometimes alumina,zirconia, alumina-magnesia, hafnia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, and boron carbide, as well as oxides of these materials. These materials form a strong chemical bond with the surface, repelling water and dust, making it easier to clean, and preventing stains.
How often should I apply wax or ceramic coating?
Waxes need to be reapplied every few months to maintain their protective layer. Ceramic coatings, on the other hand, have a longer renewal cycle, typically every 2 to 5 years. This depends on the quality of the coating and maintenance.

