Article Chapters
High-solids coatings are a perfect combination of science and technology, combining durability and environmental protection. It is not just a layer of paint applied to the wall, but a comprehensive type of coating that has completely changed the way we protect and beautify the environment. Follow me and learn about the comprehensive knowledge of high-solids coatings. If you are looking for the perfect product or supplier, don’t forget to browse our extensive directory at coatingsdirectory.com, where quality and convenience are combined.
What is High Solids Coatings?
High-solids coatings can also be called high-solids formulations. High-solids coatings are defined as one-component or two-component coatings, which generally refer to coatings formulated with higher resin concentrations and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) concentrations. High-solids coatings are composed of at least 65% solid ingredients (binders, pigments and additives). High-solids coatings can be solvent-based or water-based, and their formulations can maintain satisfactory effects or application performance.
Although there is no specific requirement for the solids content in the coating during daily painting, higher solids content usually means lower solvent content, thereby reducing VOC emissions. In contrast, solvent-based coatings are generally considered to be the main source of harmful VOCs. This despite reducing the percentage of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) to keep up with modern, increasingly stringent regulations and to protect the planet.
Advantages and Disadvantages of High Solids Coatings:
High solids content has some important advantages due to the increased solids content:
- Low VOC content (volatile organic compounds) and friendly to nature;
- Less evaporation during the drying process, making the paint surface brighter and more opaque;
- Provides longer-lasting protection, thereby saving maintenance costs;
- Better coverage;
- High-quality completion results;
- Short drying time;
- Low fire risk;
Other disadvantages compared to traditional paints are:
- High viscosity will cause difficulties when spraying;
- The initial price is higher;
- The application process requires more skills and professional knowledge;
- It is difficult to repair;
Application scenarios of high solid coatings:
High solids coatings are the Renaissance artists of the coating world, showcasing their versatility across a spectrum of canvases:
- High Solids Epoxy Coating: The stalwart defender of industrial floors, offering unparalleled resistance to abrasion and chemicals. It’s like giving your garage floor the armor of a gladiator.
- High Solids Epoxy Garage Floor Coating: Turn your garage into a showroom with this coating’s durable, glossy finish that laughs in the face of oil spills and tire marks.
- High Solids Silicone Roof Coating: This is the Gandalf of roof protections, saying, “You shall not pass!” to weather and UV damage.
- High Solids Air Dry Coating: For those who don’t like to wait, this coating dries quicker than a cheetah on a sprint, ready to protect in no time.
- High Solids Bake Coating: Like a fine soufflé, this coating rises to the occasion under heat, providing a robust and durable finish.
High-solid coatings are environmentally friendly, durable and versatile. They paint a brighter and more sustainable future for the coatings industry. So, the next time you are an environmentalist and think about choosing the right protective clothing for your surface, please give high-solid coatings a priority. After all, it is more than just a coating, it is the shield of the future.

What are the components of high-solids coating substrates?
High-solids coatings are formulated from a mix of base materials (epoxies, silicones, polyesters, polyurethanes and ceramics), pigments and additives, each of which plays a critical role in the final performance and functionality of the coating. Let’s take a closer look at the types of polymers to look out for when formulating high-solids coatings and see how these binders affect the performance and application of high-solids coatings.
- Epoxy Resins:
Epoxy resins are the Hercules of the resin world, renowned for their exceptional adhesion, chemical resistance, and durability. When used in high solids coatings, they create a fortress-like barrier against abrasion, chemicals, and moisture, making them ideal for industrial floors, pipes, and heavy-duty machinery. - Silicone Resins:
Silicone resins are the enchanters, bestowing upon high solids coatings the magic of weather and temperature resistance. They form a flexible, breathable layer that stands defiant in the face of UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and moisture. High solids silicone roof coatings, for instance, act as an impenetrable cloak, shielding structures from the relentless onslaught of the elements. - Polyester Resins:
Polyester resins bring a touch of elegance and gloss to the world of high solids coatings. Known for their excellent finish and vibrant color retention, they are the preferred choice for applications demanding a blend of aesthetic appeal and durability. From automotive finishes to decorative interiors, polyester-based high solids coatings are like the painters, adding a stroke of beauty and protection to every surface. - Polyurethane Resins:
Polyurethane resins are the chameleons, offering a balance of flexibility, durability, and resistance to chemicals and abrasion. Their versatility makes them suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive exteriors and aircraft surfaces to wooden floors and furniture. Polyurethane-based high solids coatings adapt and protect, ensuring surfaces are not just covered but also enhanced. - Ceramic Resins:
Ceramic resins are the reflective shields, designed to deflect heat and insulate surfaces. When incorporated into high solids coatings, they contribute to thermal protection, making them suitable for high-temperature environments and energy-efficient building applications.
In the field of high-solid coatings, each resin type has its own unique advantages and specialties, which affect the final appearance, performance and suitability of high-solid coatings for specific applications. If you are interested in coatings polymers, you can go to our corresponding blog to learn more information. As the industry continues to explore and understand the complex changes in chemistry and functionality, high-solid coatings are ready to protect and beautify our world with an ever-expanding library of solutions.
What the Difference Between High Solids and Low and Midium Solids Coatings?
Coatings are a diverse group of substances, each with its own unique formulation for each hue and sheen. High solids coatings differ from less concentrated low and medium solids coatings in terms of solids content, drying process and thickness. These coatings differ not only in color, but also in the nature of their presence.
- Solids content:
These are the heroes of our story. High solids generally refers to coatings formulated with higher resin concentrations and lower volatile organic compound (VOC) concentrations. High-solids paints are composed of at least 65% solids, with some of the top high-solids paints having as much as 100% solids content. These solid ingredients include base materials, pigments and additives. High solids content means less solvent is required, making these coatings guardians of efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Low and midium solids coatings, on the other hand, are specially formulated to contain more solvents. This increased solvent concentration makes the construction process easier and cheaper to manufacture. Typically, low solids means less than 30% solids; medium solids ranges from 30% to 65% solids.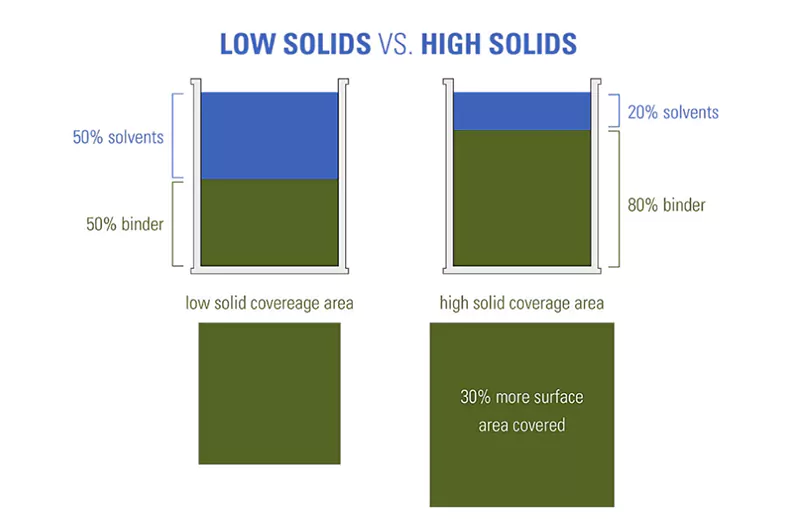
- Drying process:
Because High solids coatings have lower solvent content, less evaporation occurs, which not only speeds up the curing process but also reduces volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. It’s like an eco-magic trick, the coating transforms quickly while being kind to the environment (our environment).
And low solids and medium solids coatings: These coatings require a longer description of their drying and curing process. The drying process is a gradual process, unfolding layer by layer as more solvent evaporates. - Thickness variation:
The difference between the initial application and the thickness of the coating after curing is called the wet thickness (WT) and dry thickness (DT) of the coating. Since solvent coatings evaporate more components after application, the coverage thickness of the coating is significantly less than that of high solids coatings. An example will give you the idea: For a 40% medium solids coating it will take 2 coats to achieve the same level of thickness as a cured coat of an 80% high solids coating.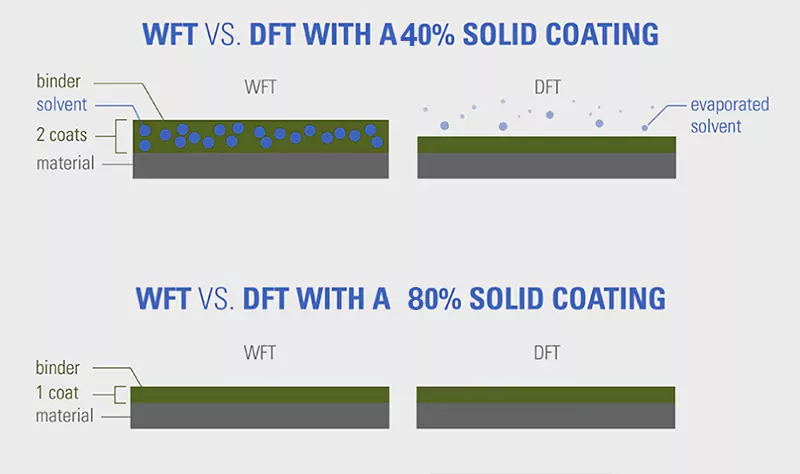
High solids and low to medium solids coatings both have their place in the coatings world, and each has its own advantages and challenges. Whether you are pursuing environmental protection or convenience, the coating field can meet your various needs.
Why is a High Solids Coatings a Good thing?
Now, let’s summarize the benefits of choosing high solids coatings. See if its product advantages match your project needs.
- Environmental Friendliness: The main advantage of high solids coatings is their ability to meet environmental standards for solvent-based paints. To address worsening air quality, the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in the United States has implemented a law limiting the amount of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) or diluents/solvents emitted into the atmosphere. High solids coatings are a new type of paint that complies with EPA emission regulations.
- Ease of Application:In situations where water-based coatings are inconvenient, high solids coatings offer the convenience of solvent-based coatings while meeting environmental requirements.
- Thickness Control: As mentioned earlier, high solids coatings have significantly lower evaporation losses after curing compared to low and medium solids coatings. Thanks to their increased solids content, high solids offer some important benefits:Less evaporation during the drying process, making the finish brighter and more opaque. Better coating coverage. Low coating consumption. Therefore, during application, high solids coatings are easier to reach the target coverage thickness.
- Convenience of Application:A major advantage of high solids coatings is that they do not require multi-step pre-treatment cleaning and painting processes. Of course, proper surface treatment is still necessary to ensure the long-term success of metal coatings.
How to Spray High Solids Coating?
Painters working with high-solids coatings need to follow the correct process, as incorrect application can negatively impact the quality and appearance of the final product. Spraying can present some challenges due to the high viscosity of these products. The higher the solids content, the more difficult it is to apply the right amount of coating.
You also need to ensure that the spraying equipment and air supply are clean and free of contaminants. You can use higher air pressure to achieve the correct atomization effect for high solids coatings.
Step-by-Step Guide to Spraying High Solids Coating:
- Prepare the Surface: Ensure that the surface to be coated is clean, dry, and free of any contaminants. Sanding or chemical cleaning may be necessary to achieve the desired surface condition.
- Prepare the Coating: Mix the high solids coating according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the viscosity is appropriate for spraying and adjust if necessary.
- Prepare the Equipment: Clean the spray gun and ensure that it is in good working condition. Check the air supply for cleanliness and proper pressure.
- Adjust the Spray Gun: Set the spray gun to the appropriate pressure and pattern for the coating being used. Test the spray pattern on a scrap piece of material if possible.
- Apply the Coating: Start spraying from one end of the surface and move in a smooth, even motion to the other end. Overlap each pass slightly to ensure full coverage.
- Apply Multiple Coats: Depending on the desired finish and the instructions from the coating manufacturer, you may need to apply multiple coats. Allow each coat to dry according to the manufacturer’s instructions before applying the next coat.
- Inspect the Finish: Once the final coat has been applied and allowed to dry, inspect the finish for any imperfections. Touch up as needed.
- Clean Up: Clean the spray gun and any other equipment used for spraying according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Dispose of any unused coating and cleaning materials properly.
Tips for Spraying High Solids Coating:
- Use proper ventilation to ensure a safe working environment.
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment, such as goggles and a respirator, to protect against fumes and overspray.
- Practice proper spraying techniques, such as maintaining a consistent distance from the surface and moving at a steady pace, to achieve an even coating.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for mixing, application, and drying times to ensure the best results.
What are the Curing Methods of High Solids Coating?
The metamorphosis of high-solids coatings from liquid to solid guardian is not unlike the mysterious rituals of ancient folklore. It takes some simple catalysis to become solid.
- Air Dry (Oxidative Cure): Air-drying high-solids coatings harnesses the power of the air itself. Oxygen reacts with the coating to form a hard, protective shell. This method is akin to letting Mother Nature do the heavy lifting, and requires patience as the air works its magic over time.
- Heat Cure: Heat cure involves subjecting the coating to high temperatures, where it becomes stronger under the constant heat.
- UV Cure: UV cure uses ultraviolet light to initiate a rapid transformation. Powerful UV rays will accelerate the cure time of high-solids coatings to the utmost. It is the most time-efficient method, combining speed with power in a dazzling display of chemistry.
There are two other common curing technologies: convection ovens and infrared radiation systems. Both are capable of consistently curing a wide range of different coatings. Each curing method offers different benefits, and their versatility offers innovative ways to achieve the ultimate protective state. When we think about how to cure high-solids coatings, there are many avenues to take.
In short, high-solid coatings currently play an irreplaceable role in shaping more sustainable, more efficient and more beautiful coating effects. They are popular in the daily painting process of homes and commercial spaces. Let coatingsdirectory.com be your guide to connect you with many professional suppliers and the latest innovations in coating technology. The success of your next project starts with the right choice, and we will ensure that you make the right choice.
Why is the market application rate of high-solid coatings not high?
High solids content coatings are more environmentally friendly, durable, cost-effective, and pose less of a threat to human health. However, the manufacturing and storage costs of developing high solids coatings are higher, and they require a higher level of technical expertise to apply.
What is high solids varnish?
High solids varnish has a higher concentration of resin and fewer solvents or VOCs (volatile organic compounds). General or lower solids polyurethane clearcoats have less resin and more solvents. The molecular structure of high solids content clearcoats is smaller than that of lower solids content clearcoats.

